How Does A Go Kart Torque Converter Work? Everything You Need To Know
A transmission is standard on most off-road go-karts and racing go-karts unless they are direct drive. An engine of a go-kart drives a rear axle via a transmission. There are usually go-karts with a clutch or torque converter.
Torque converters and clutches are long-standing competitors in the transmission industry. Each of these forms of transmission has its pros and cons without a doubt. We’ll examine which transmission is better in our showdown between a torque converter and a clutch in the go-kart. Answering this question will require you to consider what your driving habits are, as well as the purpose of the go-kart.
What is a Torque Converter?
A torque converter is required if you drive an automatic transmission vehicle, which is common in the USA.
The wheels and gears inside an automatic transmission have to be stopped while the engine keeps spinning.
It is possible for a manual transmission vehicle to do this with a clutch. There is no transmission in this situation; the engine is disconnected entirely. Automobiles with automatic transmissions employ torque converters.
One way the engine can become independent of the transmission is through the use of torque converters.
The torque converter transmits a very small amount of power when the engine is turning slowly, such as when parking in a space or going through a drive-thru.
Since the brakes need little pressure to hold, the car stays centered without much effort.
An example would be stepping on the gas in a stopped vehicle. Following a second stop, they would like to continue forward.
The car must be stopped by stepping harder on the brakes. What is the reason for this?
The reason is that when you press down on the gas pedal, the engine speeds up. The torque converter is able to receive more fluid. The wheels are thus driven with more torque.

How does a go kart torque converter work?
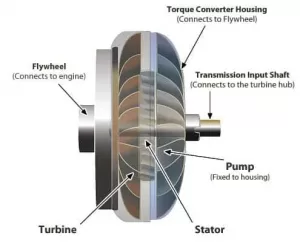
Torque converters are also housed like centrifugal clutches. An engine’s flywheel is connected to the housing through a bolt.
Turbine pumps have some fins as part of their pumps. They spin in tandem with the converter and so are attached to its housing.
Centrifugal force is used to operate the torque converter’s pump. Centrifugal pumps are used for pumping. Like a washing machine, the pump sends water and clothing out to the exterior as it spins.
Consequently, a vacuum is created which results in a movement of fluid.
Turbine blades then receive this fluid. There is a connection between this and the transmission. Turbines turn transmissions, resulting in your car’s motion.
The turbine blades have a curve. Fluid enters from the outside of the turbine. Turbines spin because the blades curve before leaving the center. Changing direction before leaving the center allows it to change direction.
When a turbine is turned on, fluid exits the center. It moved in a different direction once it entered the turbine from the outside.
At the torque converter’s dead center is the stator. As fluid from the turbine returns to the stator, it is redirected. Prior to touching the pump again, it sends it away.
In this way, a torque converter becomes more effective..
As torque converters adjust gear ratios based on engine RPM, they are great for power applications. Suitable for off-road or heavier go karts. A regular clutch, on the other hand, maintains a constant gear ratio. This makes the design appropriate for lightweight racing go-karts tuned for maximum speed.
We will examine the differences between torque converters and clutches later in this article. The following summary can serve as a quick reference.
Torque converters are commonly used for:
- You have a go-kart that goes off-road
- It’s going to be quite hectic
- Go karting is being driven by kids
- Driving at a moderate speed is your plan
Clutches are used when:
- Race go-karts are your thing
- The pace is high and you’re accustomed to it
- Go-kart racing is on your agenda
- The speed of your vehicle is moderate to high
What is a Centrifugal Clutch?
With centrifugal force, a centrifugal clutch is used to connect the engine and transmission shafts. The mechanism is located between the flywheel and the transmission.
An engine shaft is connected to the transmission by a centrifugal clutch. High speed clutches are the best option.
An engine, motor, or other driving mechanism creates centrifugal force that the clutch is completely dependent on. The clutch and the driving shaft are engaged by the centrifugal force.
Upon the engine starting, centrifugal force forces the sliding shoes outward. It becomes woven into the inner lining of the drum and leads to the movement of the drum.
Power is directly transferred from the engine shaft to the shaft which drives the transmission, then the transmission to the drum which transmits it to the load.

Parts of a Centrifugal Clutch
Here are the components that go into a centrifugal clutch so we can fully comprehend it. When you plan on repairing your own centrifugal clutch, it will be helpful to understand the components of the clutch.
- Slide shoes slide into guideways, and they slide into the shoe racks. During engagement, the friction lining will come in contact with the drum.
- At low speeds, the clutch is disengaged by the spring.
- On motors and engines, spiders can be found on the shaft. The distance between them is equal. For example, if there are four guides, each of them should be 90 degrees apart from the other. In each guide, a spring is stored for each sliding shoe.
- Friction lining is located on the outside of the outer surface of the drum – it aids in gripping the inner surface.
- During the installation of the centrifugal clutch, all parts of the clutch, such as slippers, guides, and springs, are stored in the drum. Usually, this is attached to the driving shaft of the transmission, belt, or chain.
Go-Kart Torque Converter vs Clutch
Torque Converter
- System: Belt
- Gear Ratio: Variable
- Efficiency: 80%
- Torque: Low-End
- Cost: Low to Medium
- Usage: Off-Road Go-Karts
Clutch
- System: Chain
- Gear Ratio: Fixed
- Efficiency: <100%
- Torque: High-End
- (Single disc) Low cost
Torque converters serve the same purpose as clutches. The transmissions in these two types of go-karts have distinct advantages of their own. In order to better understand them, we should take a look at how a go-kart transmission works.
Do Torque Converters Work on Go-Karts?
Torque Converter features
- About 1,500 revolutions per minute
- Two pulleys are used
- Transmission with variable speed
- Idling with no engagement
Go-karts have two transmissions popular among riders: torque converters and regular transmissions. Located on the side of the car engine, torque converters are mechanical devices. It runs on a two-pulley system, as it is shown in the image above. Located on the crankshaft, the smaller pulley is called the driver pulley. Driven pulleys are the larger pulleys.
Driver and driven pulleys are connected by a drive belt. A sprocket and a chain connect the crankshaft directly to the rear axle on traditional setups. A torque converter’s driven pulley is connected to the rear axle by chains and sprockets.
Idling results in a completely disengaged torque converter. Even though the engine is running, the go-kart stays stationary. The driver pulley begins to engage the driven pulley roughly at 1,500 RPM once the belt has clamped on the driver pulley. The rear axle and jackshaft then transmit rotational force to the go-kart.
It’s interesting to note that the ratio of gears decreases as the pulley of the driver clamps on the belt. Most gear ratios start at above 2:1, and as the RPMs increase, the lower the ratio will be until it falls below 1:1. A torque converter is an affordable device with respect to costs. In addition, clutches have a few more parts and are therefore more expensive.
What Does a Go-Kart Clutch Do?
Features of clutches
- A full 1,800 RPM is engaged
- Materials under friction push outwards
- High-speed compatibility
- It uses a roller chain and a sprocket
Alternatively, a go-kart clutch is not variable as it is fixed. As a result, the crankshaft sprocket directly affects the gear ratio and rear axle Sizes of sprockets. There is no change in gear ratio during any part of the engine’s range of RPM.
Go-kart clutches come in many different types, but the most common one is a dry centrifugal clutch. There are 4 essential components to centrifugal clutches. The internal components of the drum are enclosed by an outer drum, which you can see above. A roller chain connects the drive sprocket to the rear axle, which is attached to the drum.
In about 1,400 RPM or so, because of the centrifugal force, the spring is able to exert enough force on the friction material that it slowly starts moving outward. It is still not strong enough for the clutch to engage the drum, so it is still “slipping”.
Clutch vs Torque Converter: Differences
Torque converters operate in a completely different manner than clutches. Torque converters start engaging at about 1,700 rpm, whereas they idle first before engaging. It is variable once engaged and has a low wear rate in stop-and-go traffic. Clutches aren’t the same.
Clutches engage sooner, but are capable of slipping from 1,400 to 1,600 rpm. As a result of slipping, heat is generated and parts are worn. The clutch feels snappier, however, once fully engaged.
Therefore clutches are better suited for situations where high speeds and high torque are constantly being engaged. By contrast, torque converters are better at handling low torque ranges, as they can disengage easily at lower RPMs due to their variable gear ratio.
Overview
- At 1,700 RPM, the torque converters engage without slipping
- Around 1,400 rpm, clutches slip, slowly engaging at 1,800 rpm
- It is slightly more expensive to buy torque converters
- Too many slips or too often can wear out a clutch
- A torque converter is most effective when applied to low to middle torque ranges
- With high torque ranges, clutches are better
More About the Stator
The stator’s blade is designed aggressively to perform a specific task. By reversing transmission fluid direction, it reverses transmission fluid flow.
One-way clutches are inside the stator and the shaft. Like this, transmission shafts are fixed. The stator does not spin with the fluid because of this arrangement.
Instead, it spins counter-clockwise. When the fluid contacts the stator blades, this caused it to change direction.
Torque converters are best suited for the following applications
Torque converters work best with automatic transmissions, as you may have guessed. Other uses include industry, especially in the pharmaceutical industry transmissions of power. For example, you find such transmissions in drill rigs, conveyor belts, and forklifts.
As well as locomotives, heavy construction equipment also makes use of this mechanism. Other popular applications of torque converters include marine propulsion.
Compared to a vehicle with a manual transmission, the torque converter is less fuel efficient. Transmissions move at a different speed from engines due to this principle. Power is wasted as a result.
Compared to the same model with an automatic transmission, any manual transmission car is superior. Gas mileage will be different.
Torque converters or clutches: which is better for go-karts?
Are torque converters or clutches better? Your driving habits, in turn, should determine whether it is appropriate for its intended use. The torque converter is most commonly found in off-road go-karts due to its ability to handle low torque ranges. Low speeds make them ideal for stop-and-go operations. Go-karts on off-road tracks must often climb uneven terrain at a slower speed, due to uneven terrain.
By contrast, clutches operate faster and are more responsive. Go-kart racing lends itself well to their ability to remain engaged. Many high-performance go-karts even have multidisc clutches that can handle a wide range of torque. So, if you’re choosing between a torque converter or a clutch for your go-kart, you should decide based on what you’ll be using it for.
Final thoughts
Both have their benefits and drawbacks, as we can see. In the right context, both are excellent.
Each mechanism has its own distinctive characteristics, as you may have discovered. Our goal is to ensure that the knowledge you gain will be helpful when you need it in the future, no matter your goal.
Both torque converters and clutches have different strengths and weaknesses, as you were able to see and understand. Both transmissions perform the same function, but they work very differently, based on the type of driver and the type of go-kart you have.
High RPMs and top speeds are better achieved with racing go-kart clutches. Torque converters, however, are more typically found in off-road go-karts, which are frequently used with heavy loads and low speeds.